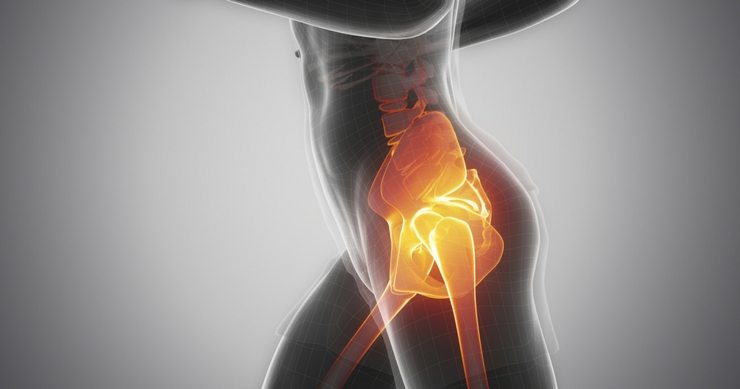
Hip Labral Tear
A hip labral tear refers to a tear in the labrum, the cartilage that lines the rim of the hip socket. This cartilage serves as a cushion, ensuring smooth movement of the hip joint.
When the labrum is damaged, it can result in pain, instability, and limited movement. It’s a condition that can affect people of all ages, but it’s especially common in athletes or individuals who engage in activities requiring repetitive hip motions.
Causes and Risk Factors for a Hip Labral Tear
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a hip labral tear:
- Trauma or Injury: A sudden fall or blow to the hip can tear the labrum. Athletes participating in contact sports, dancing, or running are at higher risk.
- Hip Impingement (Femoroacetabular Impingement): A deformity in the hip joint, where the femur and acetabulum (hip socket) don’t fit together properly, can cause friction and eventually tear the labrum.
- Repetitive Movements: Activities that involve twisting or rotating the hip joint, such as running or playing soccer, can lead to labral wear and tear over time.
- Age and Degenerative Conditions: As we age, the labrum may naturally deteriorate, increasing the risk of tears.
Symptoms of a Hip Labral Tear
Individuals with a hip labral tear often experience symptoms such as:
- Pain in the Hip or Groin: This pain can worsen with specific movements or activities.
- Clicking or Locking Sensation: Some individuals may feel or hear a clicking sound when moving the hip.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the hip freely, especially during rotation.
- Instability: A feeling of instability or weakness in the hip joint, making it challenging to stand or walk.
Treatment Options for Hip Labral Tears
Treatment for a hip labral tear depends on the severity of the injury and the individual’s overall health. Mild cases can often be managed with conservative treatments, while more severe tears may require surgical intervention.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted physical therapy exercises help strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, improving stability and reducing stress on the labrum. Stretching and strengthening routines can also enhance flexibility and mobility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as NSAIDs can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used for temporary relief.
- Stem Cell Treatment for Hip Pain: For patients who wish to avoid surgery or for those suffering from degenerative hip conditions, stem cell treatment for hip pain can be an effective alternative. This treatment uses the body’s own stem cells to repair damaged tissue and promote healing within the hip joint, offering a natural way to manage pain and improve function.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical options may be considered
Conclusion
Whether dealing with a pinched nerve in the hip or a hip labral tear, effective treatment is crucial to managing symptoms and preventing further damage. For many individuals, advanced regenerative treatments for orthopedic conditions, such as stem cell treatment for hip pain, offer promising alternatives to invasive surgery.
These therapies harness the body’s natural healing processes to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, providing relief from pain and improving joint function. By taking a proactive approach to diagnosis and treatment, you can ensure a better quality of life and enhanced mobility.
If you’re experiencing symptoms related to these conditions, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment tailored to your specific needs.